Neurons are highly polarized and interactive cells that require precise spatiotemporal regulation of their proteins for proper functioning. To achieve this, neurons can localize mRNAs for on-site and on-demand local protein production. These processes play key roles in the development, plasticity and maintenance of neurons and dysregulation of these processes are increasingly implicated in neurodegenerative diseases. However, how neurons regulate where mRNAs are localized and translated remains largely unknown. The focus of my research group is to understand the molecular mechanisms and functional relevance of how mRNA translation occurs in the right place and time in neurons in health and disease. We are interested in the role of organelles, with a specific focus on the endoplasmic reticulum, in regulating mRNA localization and local translation.
RESEARCH FOCUS
Neurons are morphologically complex and compartmentalized cells with dendrites and axons that establish dynamic connections with many other neurons, often far away from the cell body. The development, efficient functioning and survival of neurons requires careful modulation of their proteome in response to local demands. Recent research has established a crucial role for the correct localization and translation of mRNAs within axons, to allow for spatiotemporal regulation of the neuronal proteome. mRNA trafficking and local protein synthesis have been shown to be involved in a multitude of neuronal functions and dysregulation of these processes is increasingly implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). However, how neurons regulate where mRNAs are localized and translated in axons remains largely unknown.
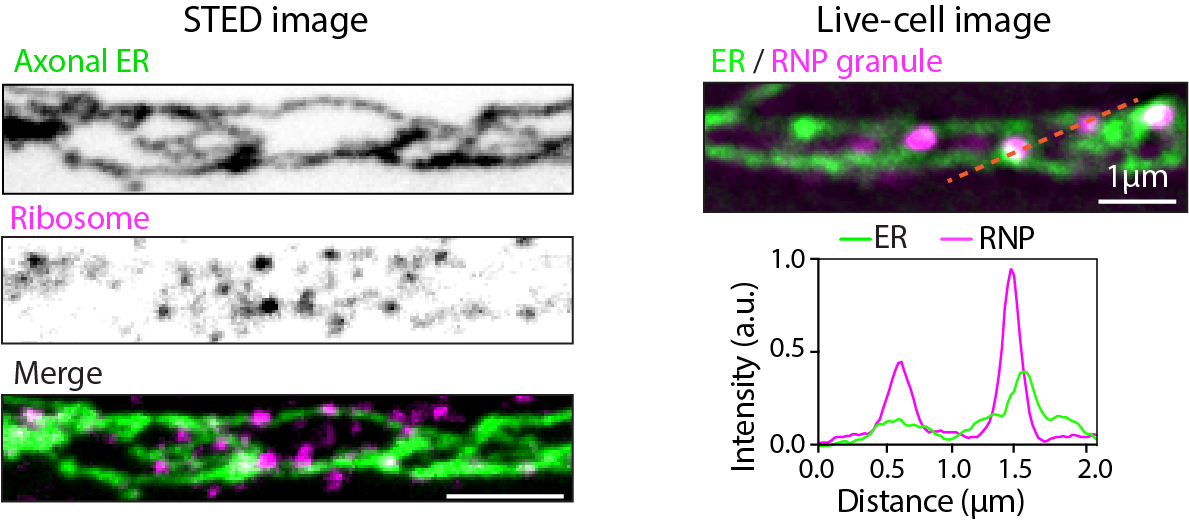
The main goal of our lab is to acquire a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms and functional consequences of mRNA localization and local translation at specific subcellular sites in neurons. We recently found that the axonal endoplasmic reticulum (ER) can bind to ribosomes and plays a role in axonal protein synthesis. Together with recent research showing the involvement of lysosomes and mitochondria in mRNA transport and translation, this raises the exciting possibility that the localization and translation of a subset of mRNAs are regulated by the ER and its contacts with other organelles to support neuron development, function and survival.
Our aim is to characterize the proteins and pathways involved in axonal ER-based translation and understand how the ER and ER-organelle contacts regulate mRNA localization and local translation in health and disease. To do so, we use live-cell and super-resolution imaging of organelles and mRNA in neurons combined with genetic engineering tools, proximity proteomics, microfluidic devices and RNA-sequencing. Together, this will allow us to understand how and to which extent the ER regulates local translation and which neuronal functions it supports in health and disease.
Open positions
We do not currently have open positions but will be looking for a PhD candidate and Postdoc to join us in 2027.
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS
Bauer VM, Koppers M. Multi-organelle-mediated mRNA localization in neurons and links to disease. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 2025; 92:102332
Koppers M*, Ozkan N, Nguyen HH, Jurriens D, McCaughey J, Dan TM Nguyen, Li CH, Stucchi R, Altelaar M, MacGillavry HD, Kapitein LC, Hoogenraad CC, Farias GG*. Axonal ER tubules regulate local translation via P180/RRBP1-mediated ribosome interactions. Developmental Cell, 2024; 59:1053-2068. *co-corresponding authors
Koppers M*, Holt CE*. Receptor-ribosome coupling: a link between extrinsic signals and mRNA translation in neuronal compartments. Annual review of Neuroscience, 2022; 45:41-61 *co-corresponding authors
Özkan N, Koppers M, van Soest I, van Harten A, Jurriens D, Liv N, Klumperman J, Kapitein LC, Hoogenraad CC, Farías GG. ER-lysosome contacts at a pre-axonal region regulate axonal lysosome availability. Nature Communications, 2021; 12(1):1-18.
Koppers M, Özkan N, Farías GG. Complex interactions between membrane-bound organelles, biomolecular condensates and the cytoskeleton. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2020; 1661
Koppers M, Cagnetta R, Shigeoka T, Wunderlich LCS, Vallejo-Ramirez P, Qiaojin Lin J, Zhao S, Jakobs MAH, Dwivedy A, Minett MS, Bellon A, Kaminski CF, Harris WA, Flanagan JG, Holt CE. Receptor-specific interactome as a hub for rapid cue-induced selective translation in axons. eLife, 2019 Nov 20;8:e48718.
Shigeoka T, Koppers M, Wong HH, Qiaojin Lin J, Cagnetta R, Dwivedy A, de Freitas Nascimento J, van Tartwijk F, Strohl F, Cioni JM, Schaeffer J, Carrington M, Kaminski CF, Jung H, Harris WA, Holt CE. On-site ribosome remodeling by locally synthesized ribosomal proteins in axons. Cell Reports, 2019 Dec;29(11):3605-3619.
Cioni JM*, Qiaojin Lin J*, Holtermann AV, Koppers M, Jakobs MA, Azizi A, Turner-Bridger B, Shigeoka T, Franze K, Harris WA, Holt CE. Endosomes serve as a platform for mRNA translation in axons and promote mitochondrial and axonal integrity. Cell, 2019; Jan; 176(1-2):56-72.e15 *co-first authors
Koppers M*, Cioni JM*, Holt CE. Molecular control of local translation in axon development and maintenance. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2018 Aug;51:86-94 *co-first authors
Koppers M*, Blokhuis AM*, Groen EJ, van den Heuvel DM, Dini Modigliani S, Anink JJ, Fumoto K, van Diggelen F, Snelting A, Sodaar P, Verheijen BM, Demmers JAA, Veldink JH, Aronica E, Bozzoni I, den Hertog J, van den Berg LH, Pasterkamp RJ. Comparative interactomics analysis of different ALS-associated proteins identified converging molecular pathways. Acta Neuropathologica. 2016 Aug;132(2): 175-96. *co-first authors
Koppers M, Blokhuis AM, Westeneng HJ, Terpstra ML, Zundel CAC, Vieira de Sá R, Schellevis RD, Waite AJ, Blake DJ, Veldink JH, van den Berg LH, Pasterkamp RJ. C9orf72 ablation in mice does not cause motor neuron degeneration or motor deficits. Annals of Neurology. 2015 Sep; 78(3):426-438.