Michel van den Oever
Associate Professor
The goal of my team is to gain mechanistic insight into the neural circuitry, cells and molecules that support persistent memories of negative and positive experiences.
Research focus:
During learning, cellular and molecular changes are induced that need to be stabilized in order for memory to be formed, stored and accurately retrieved. Collectively, the stable changes that support memory are called an engram. Although the neurobiological mechanisms that support the initial encoding and retrieval of learned associations received much attention, the processes that underlie the stabilization of new memories (days-old) into persistent remote memories (weeks-to-months-old) are poorly understood. Research by my team and others points to an important role of the cortex in expression of remote memories. However, little is known about the time-dependent functional contribution of the different neuronal sub-types in the cortex and their molecular adaptations. Our ambition is to functionally dissect the temporal, cellular and molecular organization of long-lasting associative memory in cortical circuitry. For this, we focus on memory encoding and retrieval at the level of neuronal ensembles/engram cells and are specifically interested in dissecting how different intensities or valences of experiences alter memory engram circuits.
We make use of fear conditioning with varying training intensities to study negative (aversive) experiences, and for positive experiences with distinct valences we use alcohol or sucrose self-administration in operant cages. These models have in common that they produce stable memories. Moreover, it is important to gain a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying persistent fear and alcohol memories, given the relevance for traumatic experiences and addictive behavior, respectively.
Technology: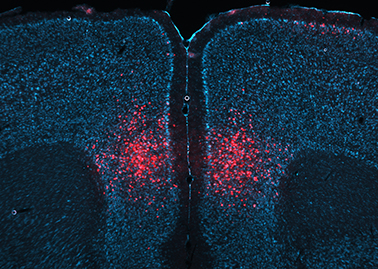 To functionally dissect neuronal circuitries involved in persistent memory formation and retrieval, we make use of viral vector approaches. In particular, chemogenetics/DREADD technology and other forms of molecular interventions are used to selectively manipulate genetically-defined neuronal subpopulations in specific brain regions. We also use these tools to connect molecular and cellular plasticity to behaviour.
To functionally dissect neuronal circuitries involved in persistent memory formation and retrieval, we make use of viral vector approaches. In particular, chemogenetics/DREADD technology and other forms of molecular interventions are used to selectively manipulate genetically-defined neuronal subpopulations in specific brain regions. We also use these tools to connect molecular and cellular plasticity to behaviour.
Collaborations:
Within the CNCR, we study molecular adaptations at the level of the synaptic engram in close collaboration with the team of Priyanka Rao-Ruiz. In addition, we investigate how astrocytes shape memory engrams in collaboration with the team of Mark Verheijen and how memory engram are impaired in Alzheimer’s disease with Ronald van Kesteren. With the team of Taco de Vries, we examine how addictive behavior is driven by activity of neuronal ensembles.
Selection of new and key publications:
Shaping Memories via Stress: A Synaptic Engram Perspective
Brosens N, Lesuis SL, Rao-Rui PR, van den Oever MC, Krugers HJ.
Biological Psychiatry (2024) DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2023.11.008
Extinction of cocaine memory depends on a feed-forward inhibition circuit within the medial prefrontal cortex
Visser E, Matos MR, Mitrić M, Kramvis I, van der Loo R, Mansvelder HD, Smit AB, van den Oever MC.
Biological Psychiatry (2022) DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.08.008
Glucocorticoids promote fear generalization by increasing the size of a dentate gyrus engram cell population
Lesuis SL, Brosens N, Immerzeel N, van der Loo RJ, Mitrić M, Bielefeld P, Fitzsimons CP, Lucassen PJ, Kushner SA, van den Oever MC, Krugers HJ.
Biological Psychiatry (2021) DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.04.010
A synaptic framework for the persistence of memory engrams
Rao-Ruiz P, Visser E, Mitrić M, Smit AB, van den Oever MC.
Frontiers Synaptic Neuroscience (2021) 13:661476.
A persistent alcohol cue memory trace drives relapse to alcohol seeking after prolonged abstinence
Visser E, Matos MR, van der Loo RJ, Marchant NJ, De Vries TJ, Smit AB, van den Oever MC.
Science Advances (2020) 6:eaax7060
Memory strength gates the involvement of a CREB-dependent cortical fear engram in remote memory
Matos MR, Visser E, Kramvis I, van der Loo RJ, Gebuis T, Zalm R, Rao-Ruiz P, Mansvelder H, Smit AB, van den Oever MC.
Nature Communications (2019) 10:2315
Engram-specific transcriptome profiling of contextual memory consolidation
Rao-Ruiz P, Couey JJ, Marcelo IM, Bouwkamp CG, Slump DE, Matos MR, van der Loo RJ, Martin GJ, van den Hout M, van Ijcken WF, Costa RM, van den Oever MC, Kushner SA.
Nature Communications (2019) 10:2232
The extracellular matrix protein brevican limits time-dependent enhancement of cocaine conditioned place preference
Lubbers BR, Matos MR, Horn A, Visser E, Van der Loo RC, Gouwenberg Y, Meerhoff GF, Frischknecht R, Seidenbecher CI, Smit AB, Spijker S, van den Oever MC.
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016) Jun;41(7):1907-16
Ventromedial prefrontal cortex pyramidal cells have a temporal dynamic role in recall and extinction of cocaine-associated memory
Van den Oever MC, Rotaru DC, Heinsbroek JA, Gouwenberg Y, Deisseroth K, Stuber GD, Mansvelder HD, Smit AB.
Journal of Neuroscience (2013) 33:18225-18233
Prefrontal cortex AMPA receptor plasticity is crucial for cue-induced relapse to heroin-seeking
Van den Oever MC, Goriounova NA, Li KW, Van der Schors RC, Binnekade R, Schoffelmeer AN, Mansvelder HD, Smit AB, De Vries TJ, Spijker S.
Nature Neuroscience (2008) Sep;11(9):1053-8.